Shabnam Zubaidullozoda
Imagine a world where you can try on clothes virtually, attend a meeting with lifelike avatars, or even surgeons with 3D overlays. Welcome to the exciting world of AR/VR—no longer science friction but a part of our everyday lives. From entertainment to retail, healthcare to education, these technologies are changing the way we interact with the digital world. Let’s explore the latest updates, trends, and use cases that are shaping AR/VR.
What is the Difference Between AR and VR?
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are both immersive technologies, but they differ in how they interact with the real world:
- AR enhances the real world by overlaying digital elements (such as images, sounds, and data) onto the physical environment, allowing users to interact with both the virtual and real world simultaneously. Popular examples include virtual try-ons for clothes or navigation apps that display directions overlaid onto real streets.
- VR, on the other hand, immerses users in a completely virtual environment, shutting out the physical world. Users typically use headsets to interact with a 3D, computer-generated environment. VR is used in gaming, virtual tours, and simulations for training.
Device Evolution
AR and VR have made significant technological advances over the past few years. Progress has been particularly remarkable in the following areas:
• Device evolution: the latest VR headsets and AR glasses offer more realistic experiences with improved resolution and reduced latency; new
devices such as the Meta Quest and Apple Vision Pro are also gaining attention.

• Real-time interaction: AR and VR enable real-time interaction with users, providing experiences beyond video calls and games. Recently, collaboration and meetings within virtual spaces are becoming more active.

Augmented Reality Applications
AR is currently applied overwhelmingly in business and enterprise use cases. Key examples include:
• Design and Architecture: AR helps designers visualize virtual products or structures in real environments and make adjustments without physical changes.
• Training and Education: Companies use AR for immersive employee training, with growing adoption in schools.
• Healthcare: AR enhances surgeries with overlays showing procedures and patient data.
• Retail: AR transforms shopping with virtual makeovers and fitting rooms.
• Marketing: AR enhances packaging, promotions, and ads for engaging customer experiences.
Virtual Reality Applications
VR is widely used in various industries, such as:
- Entertainment and Gaming: VR gaming is one of the most prominent uses of this technology, providing users with immersive experiences that feel real.
- Training and Simulation: VR is used in various sectors for simulated training. For example, pilots and surgeons use VR to practice real-life scenarios in a safe, controlled environment.
- Healthcare: Virtual reality is employed in therapy, including exposure therapy for patients with PTSD or phobias, and for pain management.
Challenges of AR/VR Technology
Despite their potential, AR and VR face several challenges. First, there are expensive hardware costs and time constraints on user adoption. Safety is also an important concern, as overuse of VR headsets can lead to motion sickness or cybersickness, which can cause symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and eye strain. These issues arise due to discrepancies between what the eyes see and what the inner ear senses. Extended use can worsen these effects.
The question of “how long is too long” when using AR/VR headsets depends on the individual. Experts recommend taking breaks every 20-30 minutes to avoid discomfort. VR users should aim to limit their sessions to around 60 minutes to prevent eye strain or fatigue.
Market Projections for AR/VR
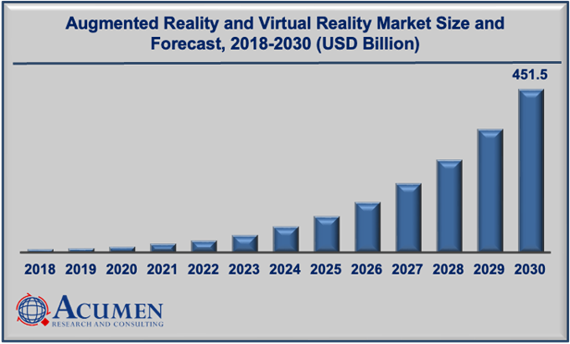
The global AR/VR market is expected to experience explosive growth, with the market size projected to exceed $300 billion USD by 2028, driven by the adoption of these technologies in industries like healthcare, education, entertainment, and more.
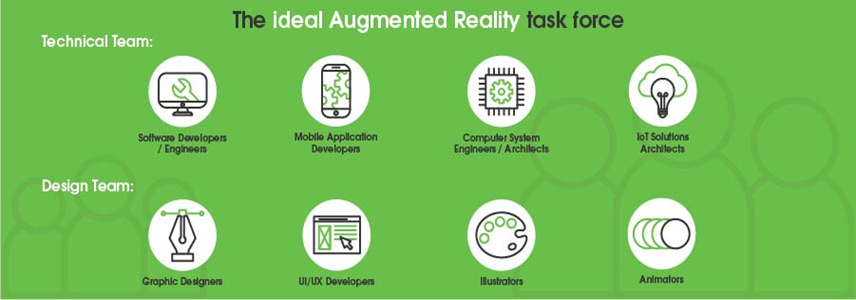
Career Paths in AR/VR for Students
As AR/VR technology continues to expand, there are several career opportunities for students and young professionals. Some potential career paths include:
- AR/VR Developer: Specializing in programming and creating AR/VR applications and experiences.
- UX/UI Designer: Focusing on designing user interfaces and experiences specific to immersive environments.
- 3D Artist/Animator: Creating realistic 3D models and animations used in VR environments.
- Product Manager: Overseeing the development of AR/VR products and ensuring they meet user needs and market demands.
Hardware Engineer: Designing the physical devices used in AR/VR experiences, such as headsets and controllers.
To pursue a career in AR/VR, students should focus on fields like computer science, software engineering, game development, graphic design, 3D modeling, and digital media. Courses in programming languages (like C++ or Unity), interactive design, and immersive technology will also be helpful.
Looking to the Future
With the full-scale spread of 5G and the development of AI technology, these issues are expected to be gradually resolved, and VR/AR will play an increasingly important role as a source of innovation that will revolutionize the way we live and work. The VR/AR market is expected to grow rapidly as new experiences and business models are created to meet the needs of companies and consumers. With a focus on the development of advanced technologies, the transformation of business through VR/AR is certain to accelerate even further.
AR/VR technology is no longer the stuff of science fiction, but is becoming a familiar part of our lives. The possibilities offered by this technology are endless and will bring about revolutionary changes in all areas, including education, medicine, and entertainment. In the near future, we may be able to experience a whole new world where reality and virtuality merge.
To learn more about AR/VR glasses click here:
References
Splunk. (2023). AR vs VR: What’s the differences? Retrieved from https://www.splunk.com/en_us/blog/learn/ar-vr.html
Stanney, K., & Salvendy, G. (2020). Motion sickness in virtual environments: An overview of research in the field. Frontiers in Virtual Reality. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvr.2020.00001
Grand View Research. (2023). Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) market size, share & trends analysis report by technology (AR, VR), by application (gaming, healthcare), by region, and segment forecasts, 2023–2028. Retrieved from https://www.grandviewresearch.com
LinkedIn. (2023). Emerging jobs report 2023. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/talent
Coursera. (2023). AR/VR specialization courses. Retrieved from https://www.coursera.org
Forbes. (2023). How 5G and AI are transforming augmented reality and virtual reality. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com